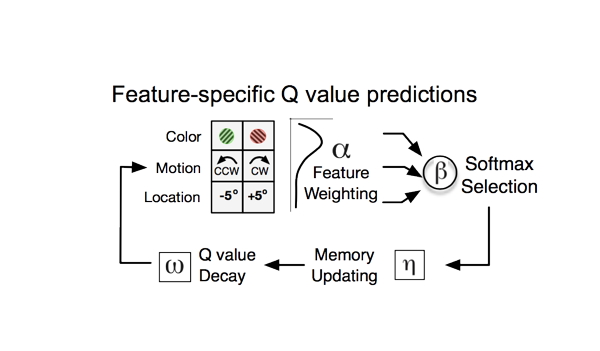
We tested which model mechanisms best explain how six animals learn attention sets and found a common set of most-important behavioral mechanisms that account for learning success.
When learning attention sets is easy value based reinforcement learning and working memory are powerful, but when learning problems are more complex learning is more efficient with attention and a meta-learning process that help speeding up learning when errors accumulate. (See our paper Womelsdorf at al. (2022) Learning at variable attentional load requires cooperation between working memory, meta-learning and attention-augmented reinforcement learning. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 34(1) 79-107.)