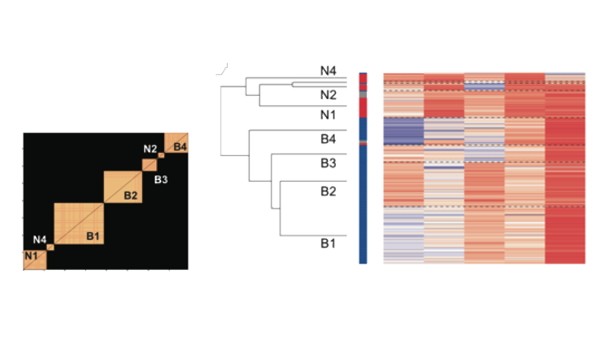
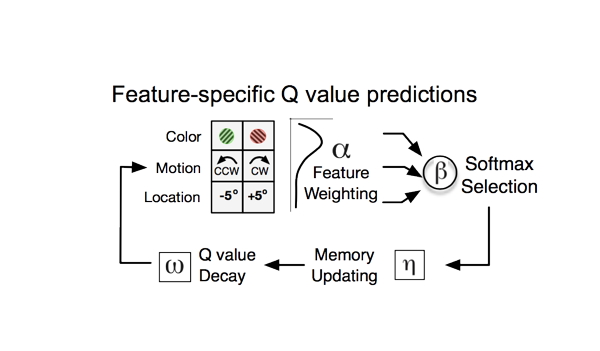
Congratulations to Ali and Mariann for the first neuropharmacological contribution from our laboratory with the article A computational psychiatry approach identifies how alpha-2A noradrenergic agonist Guanfacine affects feature-based reinforcement learning in the macaque . This study first surveys all 14 different tasks that have ever been used with Guanfacine in nonhuman primate studies and than shows in a single case study how rigorous computational reinforcement learning modelling extends existing knowledge by informing about the fundamental learning mechanisms that this drug affects during complex reversal learning. This article is particular important as it paves the way for a more formal computational approach to understand the neural effects of systemically acting psychoactive drugs like Guanfacine (which is uses in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, mild cognitive impairment, and more). Congrats Ali and Mariann and all co-authors that made this study possible!